-
NBS Tasks
Browse topics
- Monetary policy
- Financial market supervision
- Financial stability
- Banknotes and coins
- Payments
- Statistics
- Research
- Legislation
-
Publications
- Activity Report of the NBS Innovation Hub Annual Report Carbon Footprint Report of NBS Climate-related disclosures of NBS non-monetary policy portfolios Economic and Monetary Developments Financial Stability Report Investment Policy Statement of the National Bank of Slovakia Macroprudential Commentary
- Policy Briefs Report on the Activities of the Financial Market Supervision Unit Research Papers: Working and Occasional Papers (WP/OP) Statistical Bulletin Structural Challenges Other publications Sign up for your email notifications about publications
- About the Bank
- Media
- Frequently asked questions
-
For the public
Browse topics
- About the Bank
- Exchange rates and interest rates
- Banknotes and coins
- Payments
- Financial stability
- Financial market supervision
- Statistics
- Legislation
-
Publications
- Activity Report of the NBS Innovation Hub Annual Report Economic and Monetary Developments Financial Stability Report Macroprudential Commentary
- Report on the Activities of the Financial Market Supervision Unit Research Papers: Working and Occasional Papers (WP/OP) Statistical Bulletin Other publications Sign up for your email notifications about publications
- Frequently asked questions
- Media
- Careers
- Contact
NBS in the Eurosystem
The Eurosystem comprises the European Central Bank and the national central banks of the 20 countries that have adopted the euro. Národná banka Slovenska joined the Eurosystem upon entering the euro area on 1 January 2009.
The primary objective of the Eurosystem is to maintain price stability. At the same time, the Eurosystem seeks to preserve financial stability and promote financial integration in Europe.
Governing Council – the main decision-making body of the ECB. It is made up of the six members of the Executive Board and the Governors of the national central banks of the 21 euro area countries. The main tasks of the Governing Council are to adopt the guidelines and decisions necessary to ensure the fulfilment of the tasks entrusted to the ECB and the Eurosystem, to determine the monetary policy of the euro area and to take decisions in relation to the ECB’s new tasks and responsibilities in the field of banking supervision. The Governor of the NBS has been a member of the Governing Council of the ECB since the introduction of the euro in 2009.
-
Eurosystem tasks
Main tasks
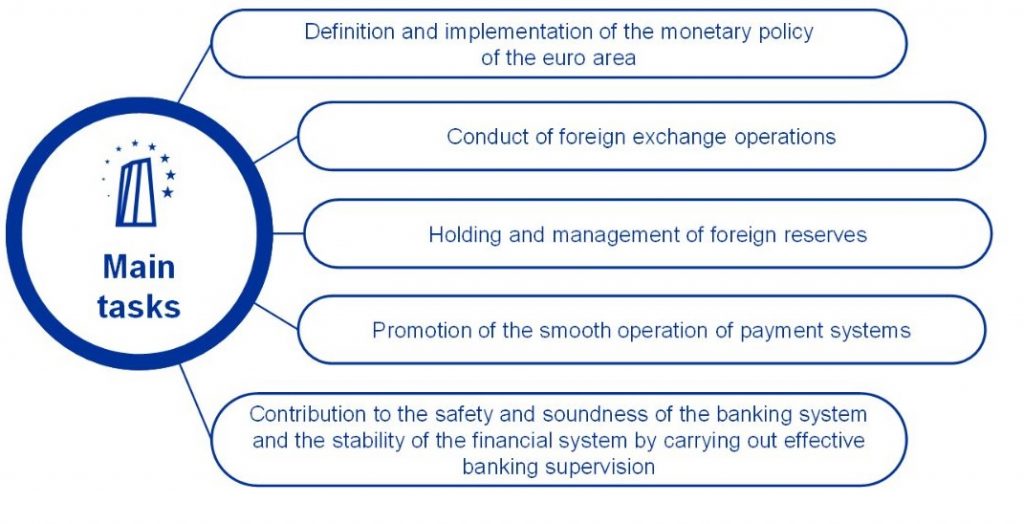
Article 105, paragraph 2, of the Treaty establishing the European Union lays down the following basic tasks:
- to define and implement the monetary policy of the euro area;
- to conduct foreign-exchange operations;
- to hold and manage the official foreign reserves of the euro area Member States (portfolio management);
- to promote the smooth operation of payment systems.
-
Tasks in more detail and additional tasks of the Eurosystem
The tasks of the ESCB and the Eurosystem are codified in the Treaty establishing the European Union (the Treaty) and in the Statute of the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) and of the European Central Bank (ECB), which is an annex to the Treaty.
The Treaty deals with the ESCB, not the Eurosystem, since it was assumed that all EU Member States would adopt the euro. Until that time comes, however, these tasks will be performed by the Eurosystem.
The primary objective of the ESCB is to maintain price stability. The Treaty further stipulates that, without prejudice to price stability, the ESCB is to support the general economic policies in the European Union with a view to contributing to the achievement of the European Union’s objectives.
The aim of the Union (Article 2 of the Treaty on European Union), is to promote a high level of employment and achieve sustainable and non-inflationary growth.
Additional tasks
Banknotes: the ECB has the exclusive right to authorise the issue of banknotes within the euro area.
Statistics: the ECB, assisted by the national central banks, collects statistical information necessary for its work from national authorities or directly from economic subjects.
Financial stability and supervision: the Eurosystem contributes to the smooth implementation of the policies of competent authorities responsible for supervising the prudential business of credit institutions and contributes to the stability of the financial system.
International and European cooperation: the ECB, in the framework of fulfilling tasks of the Eurosystem, maintains working relationships with respective institutions, authorities and forums within the EU and outside the EU.
-
European System of Central Banks (ESCB)
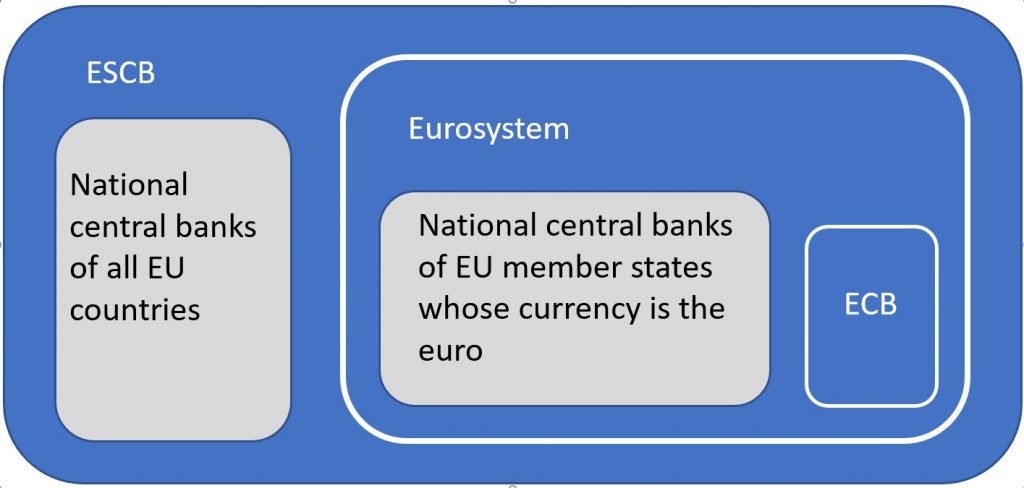
The European System of Central Banks (ESCB) comprises the ECB and national central banks of all EU Member States irrespective of whether or not they have adopted euro. Besides the euro area countries, the ESCB includes also the national central banks of countries with special opt-outs from euro area membership (Denmark) and countries with a derogation from euro area membership (Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania and Sweden). EU countries with special opt-outs or a derogation from euro area membership still have their own national currency, conduct their own monetary policy and their central banks have so far retained independence in monetary policy matters. The Eurosystem and the ESCB will exist in parallel until all EU Member States become members of the euro area (excluding countries with a special status).